A VPN is the best solution for online security because it offers a secure connection by establishing an encrypted tunnel between your device and VPN servers.
But what is a VPN tunnel, and how does it work? If the concept of VPN tunneling and its role in online security is new to you, you’re at the right place. In this article, you’ll find answers to your questions about VPN tunneling.
What is a VPN Tunnel?

A VPN tunnel is an encrypted and secure form of connection between your device (Windows, Android, etc.) and the traffic that passes through the VPN server. It hides your online identity and keeps your online identities hidden over the web, including the websites you visit and your browsing history.
A VPN tunnel is the primary function of all Virtual Private Networks. It’s called a tunnel because it creates a safe route for your data to travel between devices.
How Tunnelling Works in a VPN?
In the VPN tunneling process, your data packets are contained in the protocol’s headers to safeguard your data from any unauthorized access or interception by adding an extra layer of authentication and encryption.
After this, the VPN server and your device form a tunnel through which the encapsulated packets are transferred. The original data packets are preserved when the outer layer of authentication and encryption provided during encapsulation is removed.
The final stage involves processing and routing, where the server assigns the packets a new IP address. This makes it seem like your internet traffic is coming from the VPN server instead of your device.
With tunneling, you get a private and protected connection with your VPN, especially when connected to public networks. Additionally, building up data protects your sensitive information from leaks, including credit card information, account passwords, and other personal communication details.
Process of VPN Tunneling
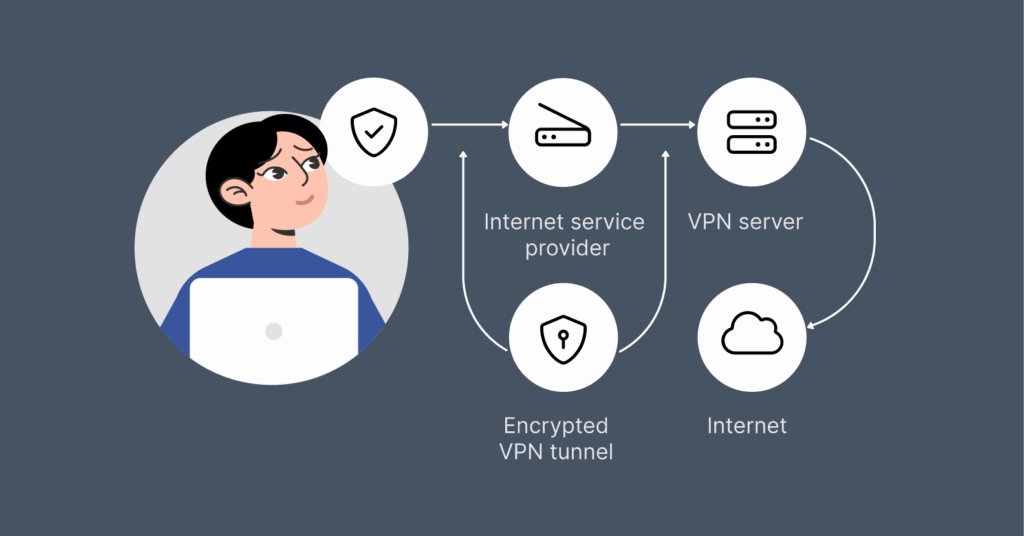
VPN tunneling isn’t a direct process, but a step-by-step procedure that starts when you connect to the VPN and ends the moment your VPN connection terminates. Let’s discuss this process in detail:
- VPN connection: It starts when you open your VPN app, choose and connect to a server. The service then begins to initiate a secure connection between your device and the VPN server.
- User verification and handshake: In this step, the user’s device and the VPN server go through an identification process. They identify each other through the user’s credentials and login information. Then they generate a cryptographic handshake — here they agree on parameters for encryption, and exchange session keys.
- Formation of the tunnel: Once the authentication completes, the VPN service creates a tunnel using protocols such as WireGuard, OpenVPN, IPSec, etc. This tunnel will keep you safe from the prying eyes of your ISP and hackers.
- Data encryption and transmission: Your device encrypts all of your data packets before passing them through the server. This step makes sure that no one else can read your information.
- Decryption at the VPN server: The VPN server receives the encrypted data transferred to it, decrypts it using the keys they both agreed to, and sends it to your desired destination (i.e., the website you’re trying to visit). Here, it changes your IP with its own, so that you remain hidden online.
- Return of the data: The site sends back the data to the VPN server, encrypts it once again, and passes it through the tunnel. Your device decrypts the data, and the website opens naturally.
- Tunnel termination: When you disconnect from the VPN, the tunnel shuts down, and all the session keys are wiped out. This makes sure that you’re safe (no traces are left behind) and no one can use the keys again in the future.
VPN Protocols with Tunnelling

Several VPN protocols use tunneling to create secure and private connections. These protocols have different speeds, security levels, and network and device compatibility configurations.
The following are some VPN protocols that use tunneling:
1. Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
This popular VPN protocol provides complete security with authentication and encryption techniques, whether encrypting the data payload in transit mode or the entire IP packet in tunnel mode, which operates at Layer 3 of the OSI model.
IPSec can be implemented through different authentication techniques, and it works with a range of encryption algorithms.
2. WireGuard
Being modern and lightweight, this protocol prioritizes simplicity, using the latest cryptographic methods to create secure connections. WireGuard is also faster and more efficient than other VPN protocols. Its user-friendly approach, solid security features, and all-around compatibility add to its growing popularity.
3. L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol over IPsec)
This protocol is usually paired together to form a safe VPN connection. It operates at the OSI model’s data link layer (also called Layer 2). The protocol uses IPsec for authentication and encryption. However, its dependence on particular protocols and ports may cause compatibility problems.
4. OpenVPN
OpenVPN is often called an open-source VPN protocol. This is because it is a user-friendly and adaptable protocol. OpenVPN uses SSL/TLS encryption to guarantee a safe connection and allows operating on multiple ports.
This makes it hard for firewalls that try to block it. The best part? OpenVPN is compatible with Linux, Windows, macOS, and mobile devices.
5. Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol
PPTP is an old VPN protocol. It is relatively fast, given its less resource-intensive encryption and position at the data link layer (Layer 2). However, its vulnerabilities make it unsuitable for handling highly sensitive information or apps.
6. SSTP
SSTP is an easy-to-use protocol with accessible support. It is relatively fast and bypasses firewalls effectively. However, it has its limitations — the protocol only works on Windows. SSTP was created in 2007 by Microsoft who has a collaboration with the NSA.
NOTE: When selecting VPN protocols, consider security, privacy, speed, and device compatibility, among other features. ExtremeVPN is a top-notch VPN service with reliable protocols for tunneling.
Security Measures Used in Tunneling

Tunneling in a VPN uses several security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized parties. These include:
Encryption
Encryption becomes necessary when the data packets are wrapped up within a tunnel. When you employ encryption algorithms like 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard) or AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), your data is carefully scrambled. This makes data interception impossible and ensures the utmost confidentiality of transmitted information.
Authentication
Authentication allows only authorized entities to receive and send data through a secure tunnel. With pre-shared keys, digital certificates, or username-password combinations, VPN protocols confirm your device and server identities.
Advanced Security Protocols
VPN protocols that employ tunneling have improved through additional measures. These protocols establish fortified connections using encryption algorithms, cryptographic keys, and other authentication methods.
Data Protection
Tunneling guarantees data protection during transmission. As a result, cryptographic hashing methods, like SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit), become useful. These algorithms verify that data packets remain intact during transmission.
The verification further ensures that the received information is precisely like the original form, ensuring data consistency and reliability.
VPN Tunneling Benefits
VPN tunneling guarantees an enjoyable internet experience because it improves accessibility, security, and privacy. The following are some benefits of tunneling:
- Improved Data Transmission: It prioritizes safe data transmission. For this reason, it employs strong encryption that protects information exchange between your device and the VPN server.
- Compatibility: A VPN tunneling protocol should work seamlessly with various devices and operating systems. This versatility ensures smooth tunneling on smartphones, routers, tablets, computers, and more.
- Bypassing geo-restrictions: It lets you bypass geo-restrictions, granting unrestricted access to the internet and censored content.
- Protecting Unsecured Networks: Using public networks exposes you to cyberattacks. However, tunneling protects your online activities, preventing malicious parties from intercepting sensitive information.
Are there Any Disadvantages of a VPN Tunnel?
Although VPN tunneling has a lot of advantages, you must know that there are certain downsides of it. These are:
- Drop in connection speed: Since the tunnel encrypts your data and passes it through the server, it can slow down your internet speed.
- Not all services allow VPNs: Some websites or platforms don’t work with VPNs; they block VPN traffic through their advanced detection systems.
Even with these drawbacks, a VPN tunnel’s security and features make it well worth using.
How to Test if Your VPN Tunnel is Established?
Before that you check if your VPN tunnel is working properly, you should confirm that your VPN encrypts and decrypts your internet traffic. Here are the three most effective ways you can check your VPN tunnel:
- Check your current IP address: Go for an IP address leak test by visiting a website and check your IP with and without a VPN. If you see that your IP changes to that of your server when you connect to a VPN, it means your VPN is working perfectly. However, this method doesn’t give you an idea if all of your traffic is encrypted by the VPN tunnel.
- Use a network monitoring software: If you want to carry out a deeper search of how your VPN tunnel is performing, a network monitoring software can help. These tools help you see exactly how your data travels — they show if your traffic is safely going through the encrypted tunnel or leaking out without protection.
- Perform a DNS leak test: A DNS leak test isn’t a direct way to test the tunnel, but it can still reveal problems. If your DNS requests go through your ISP instead of the VPN’s servers, it means some of your traffic might not be protected by the VPN tunnel.
- Ping the remote network: If you’re a bit tech-savvy, you can use the ping command to test your VPN tunnel. For this, you’ve to disconnect from the VPN and open the Command prompt if you use Windows, or Terminal if you use Linux or macOS. Type ping google.com and press Enter. This will show how fast your internet connection is. Look at the time shown in the results. Now, turn your VPN back on and repeat the process. If the ping time is a bit higher, that’s normal — it usually means your data is going through a secure, encrypted VPN tunnel.
What is VPN Split Tunneling?
A VPN split tunneling is a feature that allows you to choose which traffic you want to pass through the VPN tunnel and which you pass through the normal internet connection. This means you can select which apps or websites you want to be protected by the VPN.
For instance, some banking applications don’t work with a VPN, so you may think you need to turn off your VPN connection, but you’re wrong — just use the VPN split tunneling feature. A VPN tunnel offers so many advantages, but there may be cases when you want to turn it off.
Split tunneling is especially useful in situations where you need to access services that require your real IP address. It also comes in handy when connecting to wireless devices on your home network, like printers or smart TVs. Additionally, it allows you to exclude data-heavy apps from the VPN, which helps maintain better internet speed and performance.
Many top-notch VPN providers, like ExtremeVPN, offer a split tunneling feature, while others stick to the standard setup — full tunneling, which encrypts all your internet traffic.
Now that you’re clear on how VPN tunneling improves privacy and security, why wait longer? Join the ExtremeVPN family to enjoy a broad range of benefits while tunneling.