Despite the increasing cyber threats, proxy servers have become vital to every internet user’s life. Many organizations or offices use them to restrict users from accessing specific websites and content. However, most people don’t know much about them.
This article guides you about proxy servers and their types in detail. So, let’s get into the topic and learn what happens when you use a proxy server.
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server is a router or a system that acts as a bridge between the Internet and users. It’s somewhat similar to a VPN and helps to stream the internet without being tracked by your ISPs and other malicious entities. With a proxy server, your ISP can’t monitor your IP address and online activities.
For tech novices, an IP address is similar to your device’s home address. Each house has a unique address, so every device has a different IP. This IP address is the gateway through which hackers and criminals breach into your device or system.
Some examples of proxy servers are HTTP Proxy, SOCKS5 proxy, SSL proxy, etc. These servers change users’ IP addresses by sending their internet traffic through different servers.
What is the Function of a Proxy Server?
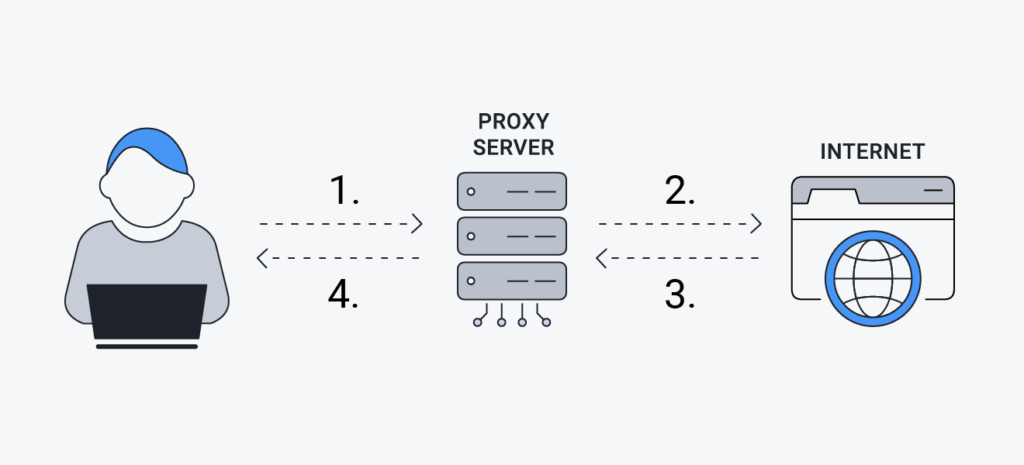
Before explaining this, let us first discuss what are the outcomes of using a proxy server.
Using the Internet without a Proxy Server
What happens when you use the web without a proxy server? In such scenarios, your device and the IP address come under the notice of various websites you’ve visited. It means whenever you browse a certain site, your IP address is exposed to the servers, and they can monitor your activities and location. These cases could initiate privacy breaches and online restrictions.
Using the Internet with a Proxy Server
Browsing the web with a proxy server adds an extra layer of protection to your security since it works as a middleman between the users and the websites you visit. As a result, whenever you visit websites, you access them through the proxy’s server location, ultimately hiding your IP address and location.
Learn about the working of a proxy server one step at a time through these steps:
- You did a search query on the internet.
- The request gets you to the proxy server first.
- It redirects your request and forwards it to the website’s servers with its IP address.
- The website’s servers respond to the proxy server with the requested data.
- After receiving the request from the website’s servers, the proxy server sends the requested data to the user.
Why Should I Use a Proxy Server?
One may question, “Do I really need a proxy server?”. And the answer is simple: yes, there are multiple reasons for it. We’re listing some of these below:
- Limits Internet Usage: Proxy servers are frequently used by many businesses and common individuals, including parents. Professionals use it to track their employees, and parents employ it to monitor their children’s activities. Moreover, some organizations use these servers to prevent users from accessing specific sites during working hours.
- Bandwidth Savings and Improved Speed: Proxy servers help organizations save bandwidth and provide better speed. They help organizations by caching (locally saving a copy of a site) popular websites. If you search for www.extremevpn.com, the proxy server will go through its locally saved copies of websites. If the server already has the most recent copy, it will send it to you quickly. This feature benefits when hundreds of users use the same proxy server to search www.extremevpn.com at a time. It only sends one request. Resulting in saving the organization’s bandwidth and providing the requested search in no time.
- Privacy Benefits: Many internet users and organizations use proxy servers to browse privately. Some users use proxies to hide their IP addresses, and others use them to identify what information is available on the website. That’s how people can easily browse the internet and access websites without telling them who made the request.
- Improved Security: Proxy servers are also known for providing security. Some proxy servers encrypt their users’ data and keep them safe from third parties. They also keep you safe from malware and viruses. In addition, organizations can use proxy servers with high-end Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) like ExtremeVPN to let their remote employee use the internet through the company’s proxy. VPNs help organizations to verify that their employees have complete access to the required websites. On the other hand, the company’s data remains safe and secure.
- Get Access to Geo-restricted Resources: If you live in a country where your favorite websites are blocked, you can bypass the geo-restriction using a proxy site (server).
Are Proxies Legal?
Using proxy servers is legal. But that depends on your usage. For example, they will be illegal if you use them for unlawful activities. However, some organizations and websites don’t allow users to use proxy servers on their premises and platforms.
Hence, it’s better to always check your country’s laws and regulations when using proxy servers. There are a few countries where these servers are prohibited.
Pros and Cons of Proxy Servers
Like VPNs and other cybersecurity tools, proxy servers have positive and negative aspects. Let’s discuss them individually.
Pros
- Anonymous Browsing: Proxy servers let you browse privately by hiding your IP addresses.
- Changing Geo-location: It helps users change their geo-location by changing their IP address.
- Security: Proxy servers provide security besides privacy. The best example of security proxies is HTTPS proxies.
- Web Filtering: Parents and organizations can use some proxies to restrict their children and employees from accessing specific sites. In addition, they can use them to monitor their online activity.
- Caching: These servers help organizations save bandwidth and provide better internet speed by caching. They save copies of famous websites and reduce the request, resulting in better internet speed.
Cons
- Lack of Encryption: Many proxies don’t provide data encryption. Cyber attackers can easily steal users’ data, credentials, and more.
- Data Logging: Some proxy servers keep the users’ information, including IP addresses and web request data. They sell it to third parties to generate revenue. Therefore, it is important to pursue the terms and conditions before use.
- Open Ports: Proxies majorly run on open ports. Cyber attackers can easily use them to attack the user’s data.
- Limited Privacy: Free proxies show ads to generate capital and bear the expenses. However, some ads contain malware and viruses that can harm your device and privacy.
- Inconsistent Speed: Everybody wants to use free proxies. Therefore, they have too much load, resulting in slow speed and server lags.
What are the Different Types of Proxies?
Different types of proxy servers are available. They are divided by their anonymity level, traffic flow, application, accessibility, service, and IPs. Below are a few common types of proxy servers.
By Traffic Flow
Forward Proxy Server
Definition:
This proxy is also known as a plain “proxy.” A forward proxy server is a middleman between the client (browsers) and the Internet. This server forwards the client’s request to the Internet servers. Then, it returns the response to the client that it received from the internet servers.
How Does it Work:
When a user submits a request, the forward proxy checks if it matches the organization’s policies. If the answer is positive, it sends the request to the website’s servers. And returns the response from those servers to the user.
Uses:
- It is mainly used by organizations to control and filter internet traffic by restricting employees from accessing specific websites or content.
- To monitor online activity for security purposes.
- Reduce bandwidth usage and increase internet performance by caching commonly accessed content or websites.
Reverse Proxy Server
Definition:
This proxy server sits between the users and the Internet servers. Its job is to forward user requests to internet servers and return responses from servers to users.
How Does it Work:
Reverse proxy servers forward user requests to the website’s servers. Servers respond according to the request and send it to the reverse proxy server. The reverse proxy server now returns the response to the user.
Uses:
- To improve the website’s security and performance.
- To reduce bandwidth usage and increase internet performance by caching popular websites.
- To filter content before accessing it.
By Anonymity Level
Transparent Proxy
Definition:
This proxy does not always change the user’s requests and responses except for identification and authentication. It performs its task without telling the user.
How Does it Work:
It forwards the user’s request to the website’s servers without telling the user. The website’s servers respond directly to the user. In this whole situation, the request sender is unaware of the proxy.
Uses:
- Mainly used by organizations to restrict and monitor their employees’ online activity.
- To increase internet performance by caching popular websites.
Note: This type of proxy doesn’t provide anonymity and privacy benefits.
Anonymous Proxy
Definition:
This proxy hides the user’s IP address from the website’s servers. It provides a high level of privacy.
How Does it Work:
When a user sends its request through an anonymous proxy, it takes the user’s request and sends it from its side. The website’s servers will see the proxy’s IP address, and the user’s IP address will remain hidden. This is how an anonymous proxy lets its users browse anonymously.
Uses:
- To bypass geo-restrictions and protect privacy.
- Some cyber attackers use it for illicit purposes, such as cyber-attacks.
High Anonymity Proxy
Definition:
A high anonymity proxy is an upgraded version of an anonymous proxy. It hides the user’s identity and presents itself as a user to the website’s servers.
How Does it Work:
When a user sends a request through a high anonymity proxy, it takes the user’s request and sends it to the website with its IP address. The proxy presents itself as a user to the website servers and keeps your identity safe.
Uses:
- To enhance online security and privacy.
- To bypass geo-restrictions and protect privacy online without revealing your identity.
- To keep yourself safe from monitoring by third parties.
By Source
Data Center Proxy
Definition:
Data center proxy changes the user’s IP addresses provided by the ISP to the IP addresses provided by data center providers.
How it Works:
It works by routing the user’s requests from various servers provided by the data center. These servers provide every user with a unique IP address and help them to browse with greater speed and anonymity.
Uses:
- To bypass geo-restriction without revealing your identity.
- To perform online tasks that need a high level of anonymity and privacy.
- To access websites in different regions for web scrapping or research purposes.
Residential Proxy
Definition:
This proxy server uses the IP addresses provided by ISPs to mask your IP address.
How Does it Work:
When a user uses a residential proxy, it takes the user’s request and masks the user’s IP address with another residential IP address.
Uses:
For social media management, web scraping, and performing various tasks that require residential IP addresses to prevent detection.
Mobile Proxy
Definition:
It uses the internet connection of a mobile device to access the internet.
How Does it Work:
When a user connects his device to the internet, the mobile proxy routes the user’s internet traffic through the mobile carrier’s network rather than the user’s ISP.
Uses:
- To bypass geo-blocking and network restrictions.
- For ad verification, web scraping, and other research purposes.
- To browse the internet more safely.
By Accessibility
Public Proxy
Definition:
Like its name, this proxy can be easily accessed by anyone online. However, many users use it, so the proxy can be slow often.
How Does it Work:
As usual, when the user sends a request to a public proxy, it sends the request to the web servers and returns the server’s response to the user.
Uses:
- To bypass geo-restrictions and content filters implemented by organizations.
- For ad verification, web scraping, and other research purposes.
- Some users utilize it for illicit purposes.
Private Proxy
Definition:
It is a proxy that only authorized users can access.
How Does it Work:
Performs a similar task to other proxies. Taking requests from authorized users and sending them to the web’s servers. Then sending the responses from the servers to the users.
Uses:
- For bypassing geo-restrictions.
- For ad verification, web scraping, and other research purposes.
- To enhance online security and privacy.
By Protocol
HTTP Proxy
Definition:
This proxy is also known as a web proxy and is very common. It handles the HTTP requests and responses between the client and the website. However, it changes the user’s IP address but doesn’t provide additional privacy and security.
How Does it Work:
After receiving the request from the user, it evaluates it. Then, it sends the request to an appropriate server. After getting the response from the server, it sends it to the user or caches it.
Uses:
- To encrypt your online traffic and mask your IP address.
- Use by organizations to restrict employees from accessing specific sites.
- To reduce bandwidth usage and improve performance by caching commonly used websites.
HTTPS Proxy
Definition:
This proxy server handles the traffic that comes from encrypted websites (HTTPS).
How Does it Work:
Whenever a user sends a request (usually encrypted), the proxy server decrypts it first. Then it fulfills the request from its caches or sends it to the server of an appropriate website. It then waits for the response. After getting a response from the server, it sends the response to the client.
Uses:
- It provides secure browsing and saves users from prying eyes.
- It is used to enforce security policies and filter web content.
SSL Proxy
Definition:
This proxy server handles the SLS/TLS connections, including HTTPS proxies.
How Does it Work:
The proxy server works by intercepting and decrypting the SLS/TLS request from the client. Then it fulfills the request from its caches or sends it to an appropriate server of the website. It waits for the response, then sends the answer to the client as soon as it gets it.
Uses:
- Organizations use them to monitor and control their employees’ internet usage and protect them from cyber threats.
- Allows organizations to inspect encrypted traffic.
- It is also used for compliance monitoring, content filtering, and solving network problems related to SSL/TLS traffic.
FTP Proxy
Definition:
This proxy server stands for File Transfer Protocol. This proxy server lies between the FTP server and a client. It controls and filters the file transfer.
How Does it Work:
The FTP proxy server receives FTP requests from the client. It sends these to an FTP server on behalf of the client. It can also perform tasks, including caching files, filtering content, and more.
Uses:
- It is mainly used by organizations to transfer files securely.
SOCKS Proxy
Definition:
This proxy server allows users to access network resources and bypass firewalls.
How Does it Work:
After the client initiates its connection with the SOCKS proxy, it sends the request to it. The proxy takes the request, sends it to the related server, and returns the response from the server to the client.
Uses:
- It helps to browse the internet anonymously.
- It works best for bypassing network and content restrictions.
SIP Proxy
Definition:
SIP stands for Session Initiation Protocol. This proxy server handles the SIP traffic among two endpoints.
How Does it Work:
When the SIP proxy server receives a client SIP request, it sends it to an appropriate endpoint. The proxy server can also perform routing tasks, changing SIP headers, and more.
Uses:
- Mostly used in calling systems like Voice over IP (VoIP) to manage call signaling.
- For security and data encryption.
Smart DNS Proxy
Definition:
This proxy server is an intermediary, directing the user’s DNS requests through remote servers. It helps users to access geo-restricted content.
How Does it Work:
When a user sends a DNS request, the Smart DNS proxy server resolves it using the DNS server first. The server it uses is available in a country where the requested content is available. That’s how the proxy server lets the user access the geo-blocked content.
Uses:
- Mainly used to access geo-blocked content on streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, etc.
DNS Proxy
Definition:
A proxy server that handles the DNS requests from the client (browser) and sends them to a designated DNS server.
How Does it Work:
When a client submits a DNS query, the DNS proxy server takes it and forwards it to an appropriate DNS server. The proxy server gets a response from the DNS server and returns it to the client.
Uses:
- To increase internet performance by reducing DNS resolution times and caching DNS requests.
DHCP Proxy
Definition:
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A proxy server that works like a gateway between the client’s DHCP request and a DHCP server.
How Does it Work:
The working of a DHCP proxy is similar to a DNS proxy server. It takes the DHCP query from the client and sends it to a suitable DHCP server. The server provides a unique IP address and forwards the response to the proxy server, which it sends to the client.
Uses:
- Commonly used to reduce the broadcast traffic on the network.
SMTP Proxy
Definition:
A proxy server that acts as a middleman between a client and an email server in the SMTP protocol.
How Does it Work:
The SMTP proxy takes the message from the email client and forwards it to the SMTP server. The server delivers the message to the recipient’s email server and sends the response to the proxy server. The SMTP proxy forwards the response to the email client.
Uses:
- To send emails securely with improved deliverability.
Are Proxy Servers Safe to Use?

The safety of proxy servers depends on the type of proxy and server configuration you use. Users must know the working principle of the proxy when they perform any web activity through it.
Proxies don’t have a no-logs policy. Therefore, they keep the users’ IP addresses, browsing history, and all online activity. If the proxies are free, there is a probability that they will sell your data to third parties, resulting in a data breach.
Many proxies don’t provide data encryption, which means any third party can see your data or online activity in plain text. You can still use these proxies, but you must compromise your privacy. We suggest you use proxy servers that provide data encryption.
If you are more cautious about privacy, use private proxy servers instead of public proxies. Only limited and authorized users can access it rather than anyone online.
We never advised anyone to use a free proxy because they don’t provide data encryption and have open access. Free proxy users have higher chances of data breaches than premium proxy users.
Therefore, use premium proxies that offer data encryption and are not accessible by anyone.
How Do I Set Up a Proxy Server?
Every operating system has a different method for setting up a proxy server.
To set up a proxy server, you must find LAN settings for your browser or operating system. You will enter the proxy server’s port number, address, and other required information there.
Mac Operating on macOS
Set up your proxy server on macOS by following these steps:

- Go to Apple settings and search for system settings.
- Click on the network option.
- Select the network service option, which is available at the right.
- Click on details and then on proxies.
- A list of proxies will appear.
- Select a proxy you want to set up and ensure you know how it works.
Apple iPhone Operating on iOS
Set up your proxy server on iOS by following these steps:

- After selecting the region and language on your new Apple device, select Set Up manually.
- During the Wi-Fi network setup, press the home button for 2 seconds.
- Click on the wifi settings.
- Tap on the option available next to your wifi network’s name.
- A list of proxy servers will appear.
- Select the required proxy server and start browsing the internet safely.
Microsoft Windows 10

Set up your proxy server on Windows by following these steps:
- Visit the start option and click on the settings.
- Select the network & internet option from the settings menu.
- Click on the proxy option from the side menu.
- Turn on the use script option.
- Enter your script address or turn on the ‘use a proxy’ option to set up a proxy manually.
Safari

Set up your proxy server on Safari by following these steps:
- Open the Safari app and open the app’s settings.
- Click on the ‘Advanced’ option.
- Open the Network setting by selecting the ‘Change settings’ option (next to proxies).
- Modify the proxy settings and enter the details that you have.
- Click OK after entering all required details.
Mozilla Firefox

Set up your proxy server on Mozilla Firefox by following these steps:
- Open settings by clicking on the menu button.
- Visit the General Panel and then click on Network Settings.
- Open the connection setting dialog by selecting the Setting option.
- Choose the option you would like.
- Click on the ‘Manual Proxy Configuration to set up a proxy manually.
Google Chrome

Set up your proxy server on Google Chrome by following these steps:
- Log into your Google Admin console.
- Click on Devices and then on Networks.
- Choose the organizational unit.
- Press the type of network configuration you want to modify or delete.
- To edit or modify the existing network configuration, click the network option and make changes.
- To remove the existing configuration, click on the remove option.
- Click on save changes.
VPN vs. Proxy Server: Are They Same?
VPNs provide end-to-end encryption, which makes them different from proxy servers. While a proxy server only forwards your request to the web’s servers on your behalf.
Proxies can help users to filter online content. However, VPNs are used to provide online security and privacy. By encrypting all of your online traffic, a VPN makes it virtually impossible for anyone else to monitor what you do online.
In other words, a VPN is like an envelope that keeps your data hidden and safe from third parties. In contrast, a proxy server is similar to a postman who reads and delivers the message.
Boost Your Online Security and Dodge Blocks With ExtremeVPN

ExtremeVPN is one of the best VPNs in the industry. It lets its users access over 6500 servers in 78+ countries. The service provides 256-bit AES encryption, the most advanced data encryption technology. It also offers a no-logs policy and provides many other security & privacy features.
ExtremeVPN redirects its users’ internet traffic through its encrypted servers. Our servers hide the users’ IP addresses and provide different IP addresses according to the servers you select. When traveling abroad, you must use a VPN to bypass regional restrictions and access your favorite streaming services from anywhere in the world.
If you still wish to use a proxy server, ExtremeVPN has the world’s fastest and most advanced proxy that you can try. With it, you can browse the internet anonymously and access geo-restricted content in no time.
